GS 2
Charting the path for the Sixteenth Finance Commission
Source: https://www.thehindu.com/todays-paper/2023-07-29/th_chennai/articleG63BI00G8-3738663.ece
Context: The Sixteenth Finance Commission is due to be set up shortly.
Relevance: GS 2 Constitutional Provisions

Impact of COVID-19 and Geopolitical Challenges:
- Significant changes have occurred since the constitution of the Fifteenth Finance Commission in November 2017.
- The COVID-19 pandemic and subsequent geopolitical challenges have had a substantial impact on the economy and government finances.
- The combined government debt-GDP ratio increased close to 90% by the end of 2020-21.
Vertical and Horizontal Dimensions:
- The Fourteenth Finance Commission increased the share of States in the divisible pool of central taxes to 42% from 32%.
- The share was revised to 41% when the number of States in India reduced to 28.
- The Centre’s fiscal imbalances were managed through the withdrawal of Planning Commission grants as the Planning Commission was abolished.
- Non-shareable cesses and surcharges need re-examination.
- Decline in States’ Share of Centre’s Gross Tax Revenues:
- During 2020-21 to 2023-24 (BE), the effective share of States in the Centre’s gross tax revenues averaged close to 31%, lower than the previous period’s share of nearly 35%.
- The increase in cesses and surcharges to 18.5% of the Centre’s GTR during 2020-21 to 2023-24 (BE) from 12.8% during 2015-16 to 2019-20 affected States’ share.
- The Sixteenth Finance Commission needs to scrutinize the heavy reliance on cesses and surcharges.
Need for Equalization and Resource Transfers:
- States’ share in the Centre’s divisible pool of taxes is determined based on indicators like population, per capita income, area, etc.
- Richer States have argued for lowering the weight given to per capita income as a determining factor.
- Attention needs to be paid to the needs of lower income States, and equalization of education and health services should be prioritized in resource transfers.
Recommendations and Reforms:
- The debt-GDP ratio for the combined account of central and State governments exceeded the corresponding FRBM norms of 40% and 20%.
- The 2018 amendment to the Centre’s FRBM needs re-examination as recommended by the Fifteenth Finance Commission.
- Setting up a loan council to oversee loan magnitudes and profiles of central and State governments may be considered.
- Scrutiny of non-merit subsidies, maintaining fiscal deficit within limits, and providing incentives for fiscal performance are essential for fiscal discipline.

Bill proposes President as Visitor to all IIMs; experts fear impact on autonomy
Source: https://www.thehindu.com/todays-paper/2023-07-29/th_chennai/articleGJ3BI0KNT-3738675.ece
Context: Union Education Minister Dharmendra Pradhan introduced the Indian Institutes of Management (Amendment) Bill in the Lok Sabha.
Relevance: GS -2 Education
Indian Institutes of Management (Amendment) Bill
- President as Visitor: The Bill proposes to make the President of India the Visitor to all Indian Institutes of Management (IIMs). The Visitor will have the authority to nominate the Chairperson of the Board of Governors of IIMs, a role currently held by the Board itself.
- Interim Board: The Bill empowers the Central government to constitute an interim Board in case of suspension or dissolution of the existing Board of Governors of IIMs.
- Impact on Autonomy: Experts believe that the proposed amendments may impact the autonomy of IIMs and subject them to governance similar to Central universities.
- National Institute of Industrial Engineering: The Bill seeks to rename the National Institute of Industrial Engineering, Mumbai as the Indian Institute of Management, Mumbai.
- Changes in Appointment Process: The Bill amends Section 16 to give more powers to the Visitor in the appointment of IIM Directors. The Board will now need prior approval from the Visitor to appoint a Director from a panel of recommended names by a search-cum-selection committee. The Visitor can also terminate the Director with prior approval.
- Deletion of Sections: The Bill deletes Section 17, which gives powers to the Board to initiate an inquiry against the Director. Section 29 on “Coordination Forum of the Institute” will also be amended.
The Bill aims to bring significant changes to the functioning and governance of IIMs by giving more authority to the President as the Visitor and centralizing the appointment process for Directors.
GS 3
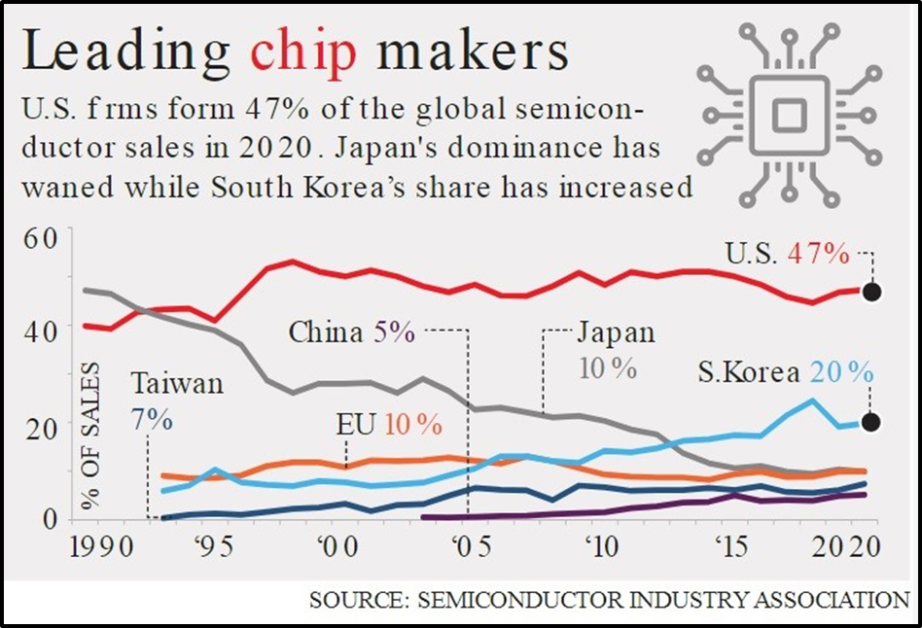
Modi says India can become hub of chip-making industry
Source: https://www.thehindu.com/todays-paper/2023-07-29/th_chennai/articleGJ3BI0G0F-3738691.ece
Context: PM Modi inaugurated the ‘Semicon India 2023’ conclave in Gujarat and made a strong pitch to global investors, asserting that India would emerge as a global hub for the semiconductor and chip-making industry.
Relevance: GS -3 Effects of liberalization on the economy, changes in industrial policy and their effects on industrial growth.
What are semi-conductors?
- Semiconductors are materials that have an electrical conductivity between that of conductors and insulators. They are characterized by their ability to conduct electricity under certain conditions but restrict it under others.
- Semiconductors are typically crystalline materials composed of atoms with four valence electrons, such as silicon (Si) and germanium (Ge).

Reforms and Incentives
- Policy Reforms: To expedite the growth of the semiconductor sector, India is continuously undertaking policy reforms and collaborating with partner countries to create a comprehensive roadmap for the industry.
- Tax Incentives: The government offers tax incentives to companies interested in setting up their semiconductor factories in the country, along with highlighting Internet penetration, fiber infrastructure, availability of talent, a huge market, and a friendly corporate tax system.

India’s Rapid Development
- Electronic Manufacturing Sector: PM Modi noted that India’s electronic manufacturing sector has witnessed significant progress, growing from $30 billion to over $100 billion. He also mentioned the rise in electronic manufacturing exports and the presence of more than 200 mobile manufacturing units in the country.
- Investment Announcements: At the ‘Semicon India’ conference, U.S. chipmaker Advanced Micro Devices (AMD) announced plans to invest around $400 million in India over the next five years and build its largest design center in Bengaluru.
- Focus on India: Taiwan-based Foxconn’s chairman, Young Liu, expressed optimism about India, focusing on the country for its plant and acknowledging the determination of the Indian government.
Need legally binding instrument to end plastic pollution: PM
Source: https://www.thehindu.com/todays-paper/2023-07-29/th_chennai/articleGJ3BI0G0D-3738692.ece
Context: Prime Minister Narendra Modi called on the G20 nations to work constructively for an effective, international legally binding instrument to end plastic pollution
Relevance: GS Paper – 3 Environmental Pollution & Degradation
Key Points from Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s Address at the G-20 Environment Ministers’ Meeting:
- Call to End Plastic Pollution: PM Modi urged G-20 nations to work together to create an international legally binding instrument to combat plastic pollution effectively.
- Progress on Climate Action: India achieved its target of installed electric capacity from non-fossil fuel sources nine years ahead of the 2030 deadline. The country is among the top five globally in terms of installed renewable energy capacity.
- Net Zero Target: India aims to achieve ‘Net Zero’ emissions by 2070, indicating the country’s commitment to address climate change and reduce carbon emissions.
- Supporting Global South: PM Modi emphasized the need for stronger action on commitments under the UN Climate Convention and the Paris Agreement to support the developmental aspirations of countries in the Global South in a climate-friendly manner.
- Ocean Conservation: Referring to Small Island States as ‘Large Ocean Countries,’ PM Modi highlighted the significance of oceans as crucial economic resources and the need for responsible use and management of oceanic resources.
Significance of Plastic:
- Versatility and Low-Cost: Plastic is a versatile, lightweight, and cost-effective material that benefits companies, consumers, and society in various applications.
- Medical Industry: Plastic is used in the medical sector to maintain sterility. Syringes and surgical implements are made from plastic for single-use purposes.
- Automotive Industry: Plastic has enabled a significant reduction in vehicle weight, leading to reduced fuel consumption and environmental impact.
- Safety Applications: Plastics are used for protective gear such as helmets and safety features in cars like seatbelts, fuel tanks, windscreens, and airbags.
Challenges Associated with Plastic-Waste:
- Single Use Plastic: Around 40% of total plastic is discarded after a single use, leading to extensive plastic pollution in the environment.
- Microplastics: Plastic waste breaks down into small particles called microplastics, which are found everywhere, even in drinking water systems and the air.
- Inadequate Waste Management: Globally, approximately one-fourth of plastic waste is not collected, leading to open burning in less wealthy countries and releasing toxic chemicals into the air.

Plastic-Waste Issues in India:
- Growing Plastic Consumption: India struggles to manage the increasing plastic waste generated daily, leading to over 10,000 tonnes of uncollected plastic waste.
- Unsustainable Packaging: The packaging industry in India is a major plastic consumer, causing significant material value loss due to unsustainable packaging.
- Online Delivery: The popularity of online retail and food delivery contributes to the rise in plastic waste, impacting the environment.
- Impact on Ecosystem and Health: Plastic waste affects marine life, enters the food chain, and poses health risks to humans due to the presence of microplastics.
India’s Efforts to Address Plastic-Waste:
- National Dashboard and Plastic Waste Management Rules: India launched awareness campaigns and introduced rules to regulate single-use plastic and promote circularity through Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR).
- India Plastics Pact: A collaborative initiative to reduce, reuse, and recycle plastics within the material value chain.
- Project REPLAN: A sustainable alternative to plastic bags to reduce consumption.
Effective Solutions to Plastic-Waste Management:
- Identifying Hotspots: Governments can identify key areas of plastic leakage and develop targeted policies to address plastic pollution.
- Designing Alternatives: Promote non-plastic, recyclable, or biodegradable materials to replace single-use plastics.
- Recycling and Innovation: Utilize plastic-eating bacteria and innovative technologies for effective plastic waste management.
- Circular Economy: Adopt circular economy principles to reduce material use and recapture waste as a resource.
Global Initiatives:
- United Nations Resolution: Countries signing a resolution to address plastic pollution and make commitments for the full life-cycle management of plastics.
- European Union Directive: The EU’s Directive on Single-Use Plastics to curb plastic pollution.
- Closing the Loop: A UN project helping cities develop inventive policy solutions to tackle plastic pollution.
- Global Tourism Plastics Initiative: A commitment to reduce plastic pollution from the tourism sector by promoting reusable, recyclable, and compostable packaging.
Land-use changes putting rocky addresses of animals under stress, shows study
Source: https://www.thehindu.com/todays-paper/2023-07-29/th_chennai/articleGJ3BI0G0H-3738690.ece
Context: The study was conducted in the Sahyadri plateaus of Maharashtra to investigate the effects of agricultural changes on biodiversity.
Relevance: GS -3 Environment
Introduction
- The focus was on elusive amphibians, insects, and reptiles that inhabit the areas under loose rocks.
- The main agricultural shift observed was the rapid transition from traditional local grain cultivation to monoculture plantations of mango and cashew, which has led to significant ecological impacts.
Key Findings:
Biodiversity at Risk:
- The study identified various species of animals, including the white-striped viper gecko, Seshachari’s caecilian, saw-scaled viper, ants, spiders, and scorpions, which live under the loose rocks.
- These animals depend on these rocky habitats for shelter, especially during extreme weather conditions like scorching heat in summer and heavy monsoon rains.
Agricultural Trends:
- Researchers observed that the traditional local grain cultivation was being abandoned in favor of establishing mango and cashew plantations.
- Unfortunately, this change in land use has resulted in the destruction of natural plateaus that provided essential habitats for these animals.
Impact on Endemic Species:
- The expansion of mango orchards has led to the conversion of more than 25,000 hectares of lateritic plateaus.
- This drastic change in the landscape has negatively impacted rare and endemic animal species, which are now facing threats to their survival due to habitat loss.
Rarity and Vulnerability:
- The study found that the animals living under loose rocks have become increasingly rare due to the expansion of orchards.
- Their vulnerability to these rapid changes in land use necessitates urgent conservation efforts to protect their habitats.
Calls for Conservation:
- Researchers emphasized the importance of preserving representative plateau habitats and stressed the need for collaboration with local communities, who are the landowners, to ensure successful conservation efforts.
Baseline Data for Conservation:
- To guide conservation efforts effectively, the study compared animal communities in plateaus, abandoned paddy fields, and orchards.
- The collected data establishes a baseline for understanding the impact of land-use changes on biodiversity.
Long-term Implications:
- The disappearance of poorly known animals from the plateaus can have cascading effects on the ecosystem’s balance.
- Preserving unique animals and their habitats is crucial for maintaining overall biodiversity.
Partnerships for Conservation:
- The study highlights the necessity of joint efforts involving researchers, local communities, and authorities to protect natural habitats and biodiversity. Collaboration is key to ensuring the sustainability of the ecosystem.
Raising Awareness:
- The study calls for urgent action to address the impacts of agricultural changes on biodiversity.
- Advocating for sustainable land-use practices and preserving vulnerable species is essential to safeguarding the delicate balance of the ecosystem.
Mercury rising
Source: https://www.thehindu.com/todays-paper/2023-07-29/th_chennai/articleG63BI00GA-3738662.ece
Context: The United Nations Secretary-General, António Guterres, this week reiterated the consequences of the climate catastrophe that has enveloped the globe.
Relevance: GS Environment
Impact of Changing Ocean Conditions:
- The Central Equatorial Pacific Ocean is transitioning from La Niña conditions to El Niño conditions, leading to rising ocean temperatures.
- This, combined with other factors, is contributing to extreme weather events like wildfires in Greece, intense heat in the United States’ Southwest, and heavy rains and flooding in north and western India.
Urgent Need for Climate Action: Despite the grim situation, Secretary-General Guterres emphasized that limiting global temperature rise to 1.5°C is still possible with immediate and dramatic climate action.
- The international community must take decisive steps to combat climate change.
- COP28 President’s Call for Ambitious Emission Cuts: Sultan Ahmed Al Jaber, the COP28 President-designate, urged the world’s largest economies to be more ambitious with emission cuts. This includes greater responsibility and commitment from countries like India to mitigate greenhouse gas emissions.
India’s Role in Climate Mitigation:
- Prime Minister Narendra Modi has pledged to make India the “third largest economy.” However, this ambition also brings pressure on India to take on a more significant share of greenhouse gas mitigation responsibilities.
- India may need to advance its net-zero commitments from 2070 to 2050 and transition to generating fossil-free electricity by 2040.
Way Forward:
- Collaborative Climate Negotiations: Climate negotiations must address contentious points to achieve meaningful progress. It is crucial for countries to collaborate and find common ground to combat climate change effectively.
- The Need for Urgent Action: Secretary-General Guterres’ warning serves as a reminder that immediate action is essential to combat the climate crisis. Governments, industries, and individuals must work together to mitigate the impacts of global warming and protect the planet’s future.
