All Four GS Papers of the UPSC Syllabus will be Uploaded Soon
Like & Subscribe for Instant Updates
Prelims & Mains Lectures
Mains Classroom Lectures
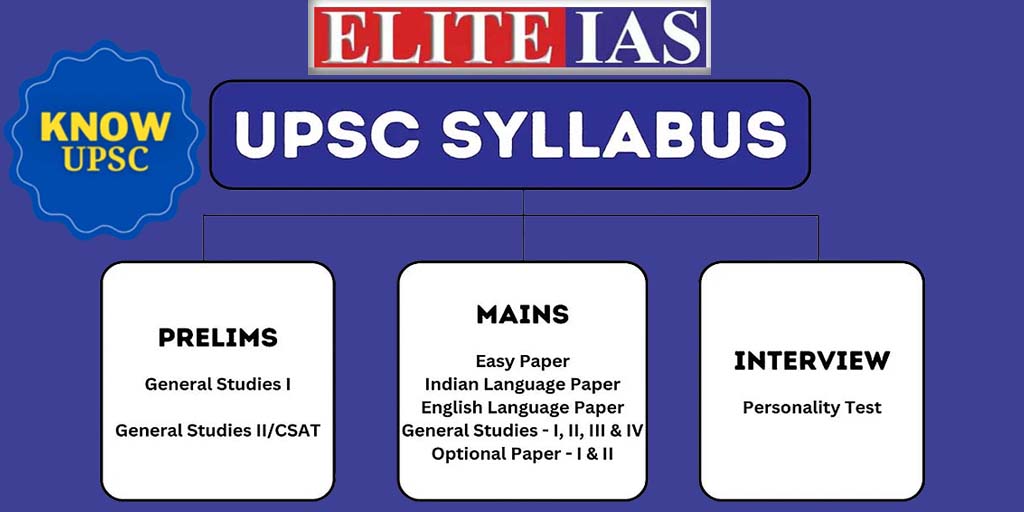
UPSC Syllabus 2026 – Prelims, Mains and Interview – Updated Syllabus For 2025-26
Management of studies during UPSC the Civil Services Examination is very critical. To properly plan and manage the studies it is essential to understand the syllabus. The Syllabus is the gateway to UPSC Prelims and Mains examinations. Syllabus provides the aspirant with the scope of the topics to be covered. The aspirants should channelize all their endeavors well to satisfies the needs of the examination. In such a scenario, the Syllabus copy guides the aspirants to follow the correct and required path.
Benefits of Understanding the Syllabus:
- When the aspirants analyse syllabus, they get know the common topics to be covered for Prelims and Mains Examinations. These points can be studied integrating the Prelims and Mains scope.
- This not only eases the preparation but also saves valuable time.
- If an aspirant keeps study without analysing the syllabus, he may end up studying relevant and useless material. In this process the aspirants will lose their most valuable time.
- To avoid this analysing the UPSC Prelims and Mains syllabus before starting the preparation is crucial.
Download UPSC Syllabus In English 2026 PDF – Click here
Download UPSC Syllabus In Hindi 2026 PDF: Click here
PRELIMS SYLLABUS:
- Among the three stages of the UPSC exam, the first stage is the Preliminary Exam.
- It comprises two papers of 200 marks each containing objective-type multiple-choice questions.
- The time allotted to attempt each exam is 2 hours which needs to be mandatorily attempted by the candidates.
- The candidates need to score qualifying marks to clear the cut-off.
- The Prelims consists of two papers of 200 marks each.
- Paper 1 consists of the General studies syllabus.
- Paper-2 (CSAT) in the Civil Services (Preliminary) Examination is a qualifying paper with minimum qualifying marks fixed at 33%.
- The question papers will be set in both Hindi and English.
You can also read: IAS Full Form
IAS Prelims exam details:
| Exam | Total marks | Duration | No. of questions | Negative Marking | Nature | Required marks to qualify |
| GS 1 | 200 | 2 hours | 100 | Yes | Marks counted for ranking | Cut-off prescribed by UPSC |
| GS 2 | 200 | 2 hours | 80 | Yes | Qualifying only | 33% (66/200) |
Prelims General Studies Paper-1 Syllabus:
- Current events of national and international importance.
- History of India and Indian National Movement.
- Indian and World Geography-Physical, Social, Economic Geography of India and the World.
- Indian Polity and Governance – Constitution, Political System, Panchayati Raj, Public Policy, Rights Issues, etc.
- Economic and Social Development – Sustainable Development, Poverty, Inclusion, Demographics, Social Sector initiatives, etc.
- General issues on Environmental Ecology, Biodiversity and Climate Change- that do not require subject specialization.
- General Science.
Prelims General Studies Paper-2 (CSAT) Syllabus:
- Comprehension.
- Interpersonal skills including communication skills;
- Logical reasoning and analytical ability.
- Decision-making and problem-solving.
- General mental ability.
- Basic numeracy (numbers and their relations, orders of magnitude, etc.) (Class X level)
- Data interpretation (charts, graphs, tables, data sufficiency, etc. – Class X level).
- English language comprehension skills – Class X level.
General Studies MAINS SYLLABUS:
- Candidates who qualify Preliminary exam are called for the Main exam.
- The UPSC mains exam is conducted in 2 parts: – qualifying papers and merit exams.
- There are a total of 9 papers in the Mains exam. Every paper is of 3 hours and extra 30 minutes extra is given to blind students.
- Paper A and Paper B are 300 marks each and the remaining papers are 250 marks each.
- The questions in Mains are of the subjective type and can be written in either Hindi or English language.
You can also read: IPS Full Form
UPSC Mains Exam pattern: –
| Paper | Subject | Duration | Total marks | Time Allotted |
| Paper A | Compulsory Indian language | 3 hours | 300 | 3 hours |
| Paper B | English | 3 hours | 300 | 3 hours |
| Paper I | Essay | 3 hours | 250 | 3 hours |
| Paper-II | General Studies I | 3 hours | 250 | 3 hours |
| Paper III | General Studies II | 3 hours | 250 | 3 hours |
| Paper IV | General Studies III | 3 hours | 250 | 3 hours |
| Paper V | General Studies IV | 3 hours | 250 | 3 hours |
| Paper VI | Optional I | 3 hours | 250 | 3 hours |
| Paper VII | Optional II | 3 hours | 250 | 3 hours |
| Sub Total | Written Test | 1750 | ||
| Personality Test | 275 | |||
| Grand Total | 2025 |
General Studies (Mains) Exam Syllabus: –
| General Studies Paper – I (Indian Heritage and Culture, History and Geography of the World, and Society) |
History –
|
| General Studies Paper – II (Governance, Constitution, Polity, Social Justice and International relations) |
Parliament and State Legislature – structure, functioning, conduct of business, powers & privileges and issues arising out of these.
|
| General Studies Paper – III (Technology, Economic Development, Biodiversity, Environment, Security and Disaster Management) |
.Issues related to direct and indirect farm subsidies and minimum support prices; Public Distribution System objectives, functioning, limitations, revamping; issues of buffer stocks and food security; Technology missions; economics of animal-rearing.
|
| General Studies Paper – IV (Ethics, Integrity and Aptitude) |
This paper will include questions to test the candidates’ attitude and approach to issues relating to integrity, probity in public life and his problem solving approach to various issues and conflicts faced by him in dealing with society. Questions may utilise the case study approach to determine these aspects. The following broad areas will be covered.
|
How to analyse the UPSC Syllabus?
- Download the Prelims and Mains syllabus from UPSC website upsc.gov.in. Besides it can be easily obtained from any IAS institutes websites.
- Understand the UPSC Prelims and Mains Syllabus separately. Find out the topics from each subject which are common for prelims as well as mains.
- Start with Mains topics from General studies (GS1, GS2, GS3, GS4) Syllabus. Pick a topic from each of the General studies Papers of UPSC. Then check the Previous Year questions of Prelims and Mains asked on the particular topic. Aspirants should check the previous year’s questions from 2013 to 2023.
- After analysing each topic, the you can prepare a comprehensive note considering the Prelims and Mains coverage. Also keep adding the relevant points from current news to make your notes more valuable.
- The aspirants should read the relevant NCERTs and revise their notes multiple times. Particularly, a quick revision of the relevant books of history, polity, geography, and macroeconomics is a must. Revise your own notes, subject-wise. Complete their revision at least two to three times in these three months.
OPTIONAL
For the Mains phase of the IAS exam, an aspirant need to pick an Optional subject of their choice. UPSC provides a list of 48 optional subjects. Among the 48 subjects one subject have to be selected as Optional. The total marks allocated for the optional subject is 500 which can make a huge difference in the overall result of the aspirant. In order to study well and secure good marks in Mains exam and to get a good rank, the UPSC aspirants should carefully analyse and choose their Optional Subject. With well-planned strategies, you can easily score well in the Bengali literature. Interest should be the prime criteria for choosing any optional.
Optional exam Pattern
- The aspirants have to appear for two optional papers of same subject which they have selected for IAS (UPSC CSE) Main Exam.
- Each paper is of 250 marks, making a total of 500 marks.
- Duration for each Optional mains paper is 3 hours.
Factors to be considered while choosing an optional Subject for UPSC Mains Exam:
- Syllabus Coverage: The aspirants should analyse the syllabus of the optional subject, to be chosen, in details. Considering the length of the Optional subjects and the General studies subjects to be covered.
- Familiarity with Subject: – Different aspirants come from different graduation streams. Choosing an optional which is completely out of familiarity will left the aspirants frustrated. The aspirants should consider their subjects of graduation and then decide the Optional subject.
- Availability of Resources: – Preparing for an Optional subject of 500 marks require a good amount resources for every topic. Besides the aspirants also needs to value – add content in the material. The aspirants should take into the consideration that how easily good study material is available for an optional subject on internet and offline mode.
- Level of Competition :- A few applicants feel a decent UPSC Optional subject is the one that has a high achievement ratio as far as various aspirants are appearing. Nonetheless, it is just incompletely evident. More than all the other things, your answer copy will be assessed based only on your answer’s understandability. Thus, pick a subject that you’re OK with.
Overlapping Syllabus: – An aspirant should consider the same topics that are to be covered from the Optional Syllabus and the General studies syllabus. The aspirants should choose the subject which have more overlapping topics. This will reduce the time to read the same topic and enhance the writing capability of the aspirant.
Civil Services Exam Syllabus For IAS Mains Optional Subjects Table
Best books for UPSC IAS Prelims and Mains Exam Preparation
- UPSC Books for General Studies Booklist for UPSC Prelims & Mains
- UPSC Books for Public Administration Optional Booklist for UPSC Mains
- UPSC Books for Sociology Optional Booklist for UPSC Mains
- UPSC Books for History Optional Booklist for UPSC Mains
- UPSC Books for Philosophy Optional Booklist for UPSC Mains
- UPSC Books for Maths Optional Booklist for UPSC Mains
- UPSC Books for Geography Optional Booklist for UPSC Mains
- UPSC Books for Anthropology Optional Booklist for UPSC Mains
- UPSC Books for Commerce and Accountancy Optional Booklist for UPSC Mains
- UPSC Books for Political Science Booklist for UPSC Mains
- UPSC Books for International Relations Booklist for UPSC Mains
UPSC Books for General Studies Booklist for UPSC Prelims & Mains
| Booklist for UPSC Prelims & Mains | |
| History | NIOS course books for classes XI and XII on – Ancient India, Medieval India, Modern India, National Movement & Contemporary World and Culture of India. A History of Ancient & Early Medieval India by Upinder Singh. India’s Ancient Past by R.S. Sharma published by Oxford University Press. History of Medieval India (800–1700 AD) by Satish Chandra published by Orient Longman. History of Modern India by Bipin Chandra (2009 Edition)India’s Struggle for Independence by Bipin Chandra & Others. From Plassey to Partition and After by Sekhar Bandopadhyaya |
| World History | The Story of Civilization, Part 2 by Arjun Dev, NCERT Contemporary World History for class XII (Old NCERT Book), Mastering Modern World History by Norman Lowe |
| Geography | Certificate Physical & Human Geography (Oxford) by Goh Cheng Leong XI Standard: (1) India – Physical Environment (2) Fundamentals of Physical Geography XII Standard: (1) India – People & Economy (2) Fundamentals of Human Geography School Atlas – Orient Black Swan |
| Social Issues | XI Standard NCERT on Indian Society (Chapters on Unity & Diversity and Population Issues), XII Standard NCERT (Chapters on Communalism, Secularism and Urban Issues such as Poverty, Housing, etc.) |
| Indian Polity | Constitution of India at Work (Class XI) NCERT Publication, Indian Polity by Laxmikant, From Government to Governance by Kuldeep Mathur, Panchayati Raj in India by Kuldeep Mathur |
| Indian Economy | Indian Economic Development XI Standard NCERT, Indian Economy by Sanjiv Verma, Introductory Macro Economics XII Standard NCERT, Economics Dictionary published by Collins & Penguin |
| Ecology & Environment | XII Standard NCERT Book on Biology (Chapters pertaining to Ecology), India Year Book (Chapters on Environment). |
| Science & Technology | VIII, IX, X Standard NCERT books on Biology, The Hindu or Indian Express Newspaper, Monthly Magazine ‘Science Reporter for Science & Technology’ |
| Ethics, Integrity & Aptitude | Ethics in Governance, ARC Report, Lexicon by Chronicle Publications, The Book on Ethics, Integrity & Aptitude published by Access Publication |
Books for Public Administration Optional
Paper 1
- Chapter-I: Introduction Mohit Bhattacharya: New Horizons of Public Administration Nicholas Henry : Public Administration and Public Affairs Special Issues of Indian Journal of Public Administration
- Chapter-II: Theories of Administration D. Ravindra Prasad, V.S. Prasad and P. Satyanarayana: Administrative Thinkers D. Gvishiani Organisation and Management: A Critique of Western Theories.
- Chapter-III: Structure of Public Organisations: R.K. Jain : Public Sector Undertakings; and Mohit Bhattacharya : New Horizons of Public Administration
- Chapter-IV: Administrative Behaviour Paul Hersey : Organisational Behaviour OR Stephen P. Robbin : Organisational Behaviour
- Chapter-V: Accountability and Control: Mohit Bhattacharya : New Horizons of Public Administration Special Issues of Indian Journal of Public Administration on Accountability
- Chapter-VI: Administrative Law: Massey :Administrative Law OR M.P. Jain :Administrative Law
- Chapter-VII: Administrative Reforms: P.R. Dubbashi : Administrative Reforms G.E. Gaiden :Administrative Reforms
- Chapter-VIII: Comparative Public Administration: Ferrel Heady : Public Administration-A Comparative Perspective OR R.K. Arora : Comparative Public Administration
- Chapter-IX: Development Administration: Ferrel Heady : Public Administration – A Comparative Perspective OR R.K. Arora : Comparative Public Administration
- Chapter-X: Public Policy : IGNOU Lessons on Public Policy R. K. Sapra : Public Policy
- Chapter-XI: Personnel Administration: O Glenn :Stahl : Public Personnel Administration S. L. Goel : Personnel Administration in India.
- Chapter-XII: Financial Administration M. J. K. Thavaraj :Public Financial Administration OR G.S. Lal :Financial Administration in India IGNOU Lessons on Financial Administration
Paper 2 Indian Administration
- Chapter-I: Evolution of Indian Administration B.N. Puri Administrative History of India (Vol. I, II and III)
- Chapter-II: Constitutional Framework D. D. Basu An Introduction to the Constitution of India
- Chapter-III: Union Government and Administration A. Avasthi Central Administration
- Chapter-IV: State Government and Administration J.D. Shukla State Administration
- Chapter-V: District Administration T.N. Chaturvedi District Administration; and Special Issue of Indian Journal of Public Administration on District Administration
- Chapter-VI: Local Government S.R. Maheswari Local Government in India
- Chapter-VII: Public Sector in India R. K. Jain Public Sector Undertakings Annual Survey on Public Sector of Department of Public Enterprises
- Chapter-VIII: Public Services S.L. Goel Personnel Administration in India
- Chapter-IX: Control of Public Expenditure M. J. K. Thavaraj Financial Administration IGNOU Lessons on Financial Administration
- Chapter-X: Administrative Reforms P.R. Dubbashi Administrative Reforms S. R. Maheswari Administrative Reforms Special Issue of Indian Journal of Public Administration on Administrative Reforms
- Chapter-XI: Machinery for Planning A. Avasthi Central Administration
- Chapter-XII: Administration of Law-and-Order K. K. Sharma Law and Order Administration in India K. J. Guha Roy, District Policing
- Chapter-XIII: Welfare Administration Annual Reports of Department of Social Welfare
- Chapter-XIV: Major Issues in Indian Administration Special Issue of Indian Journal Public Administration on Indian Administration, Retrospect and Prospect and on Good Governance.
Books for Sociology Optional:
Paper 1
- Herton and Hunt, Sociology
- Mcgraw- Hill International, Singapore 1984
- Abrahamson Mark, Urban Sociology
- Prentice-Hall Inc, Englewood Cliffs, N.J., 1980
- Haris C. C., The Sociology Enterprises: A Discussion of Fundamental Concept
- St. Martin Press Inc., New York, 1980
- Wilson John, Introduction to Social Movements
- Basic Books, NY , 1998
- Hamilton , Malcom, B. The Sociology of Religion
- Routledge, London , 1995
- Williams, Malcom, Science and Social Science: An Introduction
- Routledge, London , 2000
- D.K.S. Roy, Social Development and the Empowerment of Mariginalised Groups: Perspectives and Strategies
- Sage, New Delhi – 2001
- Harris C.C., The Family
- Allen and Unwin, London – 1977
- Andreas Hess, Concept of Social Stratification, European and American Models
- Palgrave, Houndmills, NY , 2001
- Giddens, Anthony, Capitalisation and Modern Social Theory
- University Press Cambridge, 1971
- Smelser, N.J.The Sociology of Economic Life
- Prentice Hall, New Delhi – 1988
- Haralombos, M, and Heald, R,M. Sociology : Themes and Perspectives
- Randall Collins, Theoretical Sociology
- Harcourt Brace and Company, Florida, 1996
- Bottomore. T.B. Sociology : A GFuide of problem and Literature
- Allen and Unwin, London – 1972
- Etzioni, Amitali, Modern Organization
- Prentice Hall, NY, 1995
- Cuff, Sharrock, and Francis, Perrspective in Sociology
- Routledge, NY 1995
Paper 2
- Mandelbaum, David, Society in India
- Srinivas M N Caste in Modern India and Other Essays
- Asia Publishing House, Bombay -1962
- Srinivas M N Social Change in Modern India
- Berkeley,University of California Press 1966
- Srinivas and Shah, The Myth of the self sufficiency of the Indian Village
- Beteille Andre Sociology
- Beteille Andre, The idea of Natural, Inequality and other Essays
- Beteille Andre, Essay in Contemporary Sociology
- Beteille Andre, Social Inequality of Indian Penguine
- Singh Yogender Cultural Change in India
- Singh Yogender, Modernization of Indian Tradition
- Thompson Press, New Delhi – 1973
- Unnithan T K , Indra Dev and Singh, Y, (eds) Towards a Sociology of Culture in India
- Gupta, Dipasnkar, Interrograting Caste
- Shah A M Family in Contempory India
- Orient Longman, New Delhi – 2001
- Chandrani and Chandrani, Essay in Rural Sociology
- Desai, Neera, and Krishnaraj, Women and Society in India
- Singer Milton and Cohen B.S. Structure and chasnge in Indian Society
- Weener Grin Foundation for Anthropological Research 1968
- Sharma K L (ed) Sociology Inequalities in Indian, Profiles of Caste Class, Power and Social Mobility
- Rawat, Jaipur 19945
- Gallenter Masrc, Competing, Inequalities
- Oxford, NY 1998
- Joshi, P C Sociol Science and Development: Quest for Relevance
- Hasr-Anand Publication, Delhi 1995
Books for History Optional:
Booklist for UPSC History Optional
- NCERT (Class IX to XII)
- NIOS/IGNOU Notes
- India’s Ancient Past by R. S. Sharma.
- History of Medieval India: From 647 A.D. to the Mughal Conquest by Satish Chandra.
- History of Modern India by Bipan Chandra.
- India’s Struggle For Independence by Bipan Chandra.
- Indian Art and Culture by Nitin Singhania.
- A History of Ancient and Early Medieval India: From the Stone Age to the 12th Century by Upinder Singh
- From Plassey to Partition and After A History of Modern India by Sekhar Bandyopadhyay
- A Comprehensive History of Medieval India: From Twelfth to the Mid-Eighteenth Century by Farooqui Salma Ahmed
- Contemporary India: Economy, Society, Politics by Neera Chandhoke
- A History of Modern World by Jain and Mathur
- Mastering Modern World History by Norman Lowe
Books for Philosophy Optional:
Paper 1
- W. T. Stace: A Critical History of Greek Philosophy (Plato and Aristotle).
- Copleston: A History of Philosophy (Relevant Chapters from volume I, IV, V, VI, VII, VIII, IX & XI).
- Anthony Kenny: A New History of Western Philosophy. OUP Oxford.
- Datta & Chatterjee: An Introduction to Indian Philosophy. Rupa Publishing.
- C. D. Sharma: A Critical Survey of Indian Philosophy. MLBD.
- Oxford Dictionary of Philosophy.
Paper 2
- John Hick: Philosophy of Religion.
- Michael B. Wilkinson: Philosophy of Religion: An Introduction.
- O. P. Gauba: Social & Political Philosophy.
- Political Theory, An Introduction. Edited By Rajeev Bhargava & Ashok Acharya.
- Oxford Dictionary of Politics.
Books for Philosophy Optional
Paper 1
- W. T. Stace: A Critical History of Greek Philosophy (Plato and Aristotle).
- Copleston: A History of Philosophy (Relevant Chapters from volume I, IV, V, VI, VII, VIII, IX & XI).
- Anthony Kenny: A New History of Western Philosophy. OUP Oxford.
- Datta & Chatterjee: An Introduction to Indian Philosophy. Rupa Publishing.
- C. D. Sharma: A Critical Survey of Indian Philosophy. MLBD.
- Oxford Dictionary of Philosophy.
Paper 2
- John Hick: Philosophy of Religion.
- Michael B. Wilkinson: Philosophy of Religion: An Introduction.
- O. P. Gauba: Social & Political Philosophy.
- Political Theory, An Introduction. Edited By Rajeev Bhargava & Ashok Acharya.
- Oxford Dictionary of Politics.
Books for Commerce and Accountancy Optional:
Books for Commerce optional Paper I
- Accounting Corporate Accounting – Naseem Ahmed
- Accounting Standards- D. S. Rawat
- Auditing Students’ Guide to Auditing- Aruna Jha
- Income Tax book by- V.K. Singhania or Girish Ahuja
- Cost Accounting; Theory & Problems- Maheshwari & Mittal
- Financial Management
- Taxation- Income Tax, Service Tax & VAT
- Financial Management; Text and Problems- Khan and Jain
- Financial Markets & Institutions
- Indian Financial System- M.Y. Khan
- Financial Institutions & Markets- L.M. Bhole
Books for Commerce optional Paper II
- Human Resource Management- C.B. Gupta
- Industrial Relations- T.N. Chabra and R.K. Suri
- Dynamics of Industrial Relations- C.B. Mamoria and Satish Mamoria
- Human Resource Management- K. Aswathappa
- Organisation Theory and Behaviour- B.P. Singha and T.N. Chabra
- Organization Behaviour- L.M. Prasad
UPSC Books for Political Science:
Books For Political Science Paper I
- An Introduction To Constitution- D.D. Basu
- An Introduction To Political Theory- O.P Gauba
- Fifty Major Political Thinkers- Ian Adams And R W Dyson
- A History Of Political Thought: Plato To Marx – Subrata Mukherjee And Sushila Ramaswamy
- An Oxford Companion To Politics In India – Niraja Gopal Jayal And Pratap Bhanu Mehta
- Foundations Of Indian Political Thought- V.R Mehta
- A New Look At Modern Indian History- B.L Grover And Alka Mehta
- India’s Struggle For Independence – Bipan Chandra
- Indian Government And Politics – B L Fadia
Books For Political Science Paper-II
- India’s Foreign Policy – V P Dutt
- International Organisations- Spectrum Books Publication
- International Relations – V N Khanna
- Challenge And Strategy: Rethinking India’s Foreign Policy- Rajiv Sikri
- Does The Elephant Dance? Contemporary Indian Foreign Policy- David M. Malone
- Global Politics- Andrew Heywood
- MPS-004 Comparative Politics: Issues And Trends By Expert Panel Of GPH
UPSC Books for International Relations:
Books for Paper I
- An Introduction To Constitution by D.D. Basu
- An Introduction To Political Theory by O.P Gauba
- Fifty Major Political Thinkers by Ian Adams And R W Dyson
- A History Of Political Thought: Plato To Marx by Subrata Mukherjee And Sushila Ramaswamy
- An Oxford Companion To Politics In India by Niraja Gopal Jayal And Pratap Bhanu Mehta
- Foundations Of Indian Political Thought by V.R Mehta
- A New Look At Modern Indian History by B.L Grover And Alka Mehta
- India’s Struggle for Independence by Bipan Chandra
- Indian Government And Politics by B L Fadia
Books for Paper II
- India’s Foreign Policy by V P Dutt
- International Organisations by Spectrum Books Publication
- International Relations by V N Khanna
- Challenge And Strategy: Rethinking India’s Foreign Policy by Rajiv Sikri
- Does The Elephant Dance? Contemporary Indian Foreign Policy by David M. Malone
- Global Politics by Andrew Heywood
Books for Maths Optional
Books for Mathematics Paper I
- Linear Algebra – K.C. Prasad, K B Datta
- Calculus – Shanti Narayan Integral Calculus
- Differential Calculus
- Vector Calculus
- Analytic Geometry – Shanti Narayan, HC Sinha, DK Jha and Sharma
- Ordinary Differential EQs:- MD Raising Lumina, Golden series-NP Bali
- Dynamics, Statistics, and Hydrostatics – M.Ray
- Vector analysis – Shanti Narayan
Books for UPSC Maths Optional Syllabus Paper II
- Algebra – K C Prasad, KB Datta
- Real Analysis – Shanti Narayan, Royden
- Complex Analysis – GK Ranganath
- Linear Programming – SD Sharma
- Partial Diff.eqs. – Singhania
- Numerical analysis and Computer Prog. – V. Rajaraman, SS Shastri
- Mechanics & Fluid dynamics – AP Mathur, Azaroff Leonid
Books for Geography Optional Booklist
Paper 1
- A Geography by Population – R.C. Chandna
- Agricultural Geography – Majid Husain
- Climatology – D.S.Lal
- Economic and Social Geography – Made Simple – R.Knowles & J.Wareing
- Economic Geography- Hartshorn & Truman A
- Environmental Awareness – R.C.Chandna
- Environmental Geography – Savindra Singh
- Environmental Geography – H M Saxena
- General Climatology – Critchfield
- Geomorphology – Savindra Singh
- Human Geography -Majid Husain
- Oceanography- Sharma & Vatal, NCERT
- Evolution of Geographic Thought-Majid Husain
- Physical Geography – Made Simple – Richard H Bryant
- Physical Geography – Savindra Singh
- Introducing Physical Geography – Alan Strahler
- Physical Geography in Diagrams -Bunnett
- Political Geography -R.D.Dixit
- Principles of Geomorphology-W.D. Thornbury
- Regional Planning in India – Chand & Puri
- Urbanization & Urban Systems in India- R. Ramachandran
Paper 2
- A Geography of India -Gopal Singh
- Agriculture Geography – Majid Husain
- Certificate Physical and Human Geography – Goh Cheng Leong
- Economic and Commercial Geography of India – C.B. Mamoria
- Economic and Commercial Geography of India – Sharma & Coutinho
- Economical and Commercial Geography of India – C.B. Mamoria
- Environmental Awareness – R.C.Chandna
- Environmental Geography – Savinder Singh
- Environmental Geography – Saxena
- Geography of India – Majid Husain
- Geography of Population- R.C.Chandna
- Hindu’s Survey on Agriculture
- Human Geography – Majid Husain
- India Disasters Report
- Oxford School Atlas – Oxford
- Modern Political Geography of India – B.L. Sukhwal
- Regional Planning in India – Chand and Puri
- Urbanization and Urban Systems in India – R. Ramachandran
- Environmental Geography – Saxena
Books for Anthropology Optional
Anthropology books for UPSC optional:
- Physical Anthropology – P Nath
- Fossil Evidence – S Das
- Social Anthropology – DN Majumdar & T N Madan
- Indian Anthropology – Nadeem Hasnain
- Anthropology Theories – Makhan Jha
You can also read: IAS Interview
UPSC 2024 Exam Highlights | Civil Services Examination
| Name of the Exam | UPSC Civil Services Examination, 2024 |
| Conducted by | Union Public Service Commission |
| Level | National |
| Exam Frequency | Annual |
| Mode of the Exam | Pen and Paper Mode/Offline |
| Test Centres | Across Nation |
| Exam Stages | 03 Stages- Preliminary Exam, Main Exam, and Personality Test |
| Application Fee | 100/- |
| Official Website | https://www.upsc.gov.in/ |
Important Dates for UPSC CSE 2024 | UPSC Notification 2024
| Event | Date |
| Release of UPSC Notification 2024 | 14/02/2024 |
| UPSC Online Registration for UPSC CSE 2023 (Begins on) | 14/02/2024 |
| Deadline to Apply for UPSC CSE 2024 | 29/02/2024 – 6:00 pm |
| UPSC CSE Prelims 2024 Exam | 26/05/2023 (Sunday) |
| UPSC CSE Prelims 2024 Result | July |
| UPSC Exam Date 2024- CSE Mains Exam | 20 September 2024 (days) |
UPSC Posts – 3 Types of Civil Services
- All India Civil Services
- Indian Administrative Service (IAS)
- Indian Police Service (IPS)
- Indian Forest Service (IFoS)
- Group ‘A’ Civil Services
- Indian Foreign Service (IFS)
- Indian Audit and Accounts Service (IAAS)
- Indian Civil Accounts Service (ICAS)
- Indian Corporate Law Service (ICLS)
- Indian Defence Accounts Service (IDAS)
- Indian Defence Estates Service (IDES)
- Indian Information Service (IIS)
- Indian Ordnance Factories Service (IOFS)
- Indian Communication Finance Services (ICFS)
- Indian Postal Service (IPoS)
- Indian Railway Accounts Service (IRAS)
- Indian Railway Personnel Service (IRPS)
- Indian Railway Traffic Service (IRTS)
- Indian Revenue Service (IRS)
- Indian Trade Service (ITS)
- Railway Protection Force (RPF)
- Group ‘B’ Civil Services
- Armed Forces Headquarters Civil Service
- DANICS
- DANIPS
- Pondicherry Civil Service
- Pondicherry Police Service
All India Services
| Indian Administrative Service (IAS) | One of the three All India Services is the Indian Administrative Service. The Indian Administrative Service (IAS) is the permanent arm of the Indian government and state governments. The IAS cadre is in charge of formulating and enforcing government policies. The Indian Administrative Service (IAS) is India’s administrative civil service that serves the whole country. The IAS probationers start their training at Mussoorie’s LBSNAA. |
| Indian Police Service (IPS) | Indian Police Service is the one among the three All India Services. IPS officers are trained at Sardar Vallabhbhai Patel National Police Academy in Hyderabad. The IPS officers occupy senior positions in Police service. The IPS officers occupy senior positions in RAW, IB, Central Bureau of Investigation (CBI) etc. |
| Indian Foreign Service (IFS) | IFS officials are trained at LBSNAA before moving on to the Foreign Service Institute in New Delhi. It is one of the most popular civil services in the Group ‘A’ category. IFS officers are in charge of India’s international affairs. High Commissioners, Ambassadors, India’s Permanent Representative to the United Nations, and Foreign Secretaries are all possible career paths for IFS officers. A candidate who is accepted into the IFS programme is not eligible to return for the Civil Service Exam. |
| Indian Forest Service (IFoS) | One of the three All India Services is the Indian Forest Service (IFoS). Director General (DG) of Forests is the highest rank held by IFoS personnel serving in the Central Government. Principal Chief Conservator of Forests is the highest rank held by IFoS personnel working for the State Government. The Ministry of Environment, Forests, and Climate Change oversees the Indian Forest Service Cadre. Officers of the IFoS have the chance to work for a variety of organisations, including the Food and Agricultural Organization (FAO). |
| Indian Revenue Services | On a macro level, the Indian Revenue Services include functions such as revenue collection, development, and allocation, as well as security and governance. The officer in charge of this service is in charge of tax administration, as well as the creation and execution of tax and revenue policies, as well as revenue investigations. |
| Indian Railway Traffic Services | Candidates who are selected for this civil service must complete a Railway Foundation Course as well as specialised training in order to serve the Indian railways in important managerial positions. This service’s executives are in charge of passenger transportation as well as the manufacture and sale of goods and output via rail transportation. |
| Indian Audit and Accounts Service (IA&AS) | One of the most popular Group ‘A’ civil services is the IA&AS. They begin their education at the NAAA in Shimla. The Comptroller and Auditor General is in charge of this group (CAG). The financial auditing of the Central Government, State Governments, and Public Sector Undertakings is performed by this cadre (PSUs). |
| Indian Civil Accounts Service (ICAS) | This cadre is part of the civil service’s Group ‘A’. They are overseen by the Ministry of Finance. The Controller General of Accounts is in charge of this group. They received their education at the Faridabad-based National Institute of Financial Management (NIFM) and the Institute of Government Accounts and Finance. |
| Indian Corporate Law Service (ICLS) | The Ministry of Corporate Affairs is in charge of Group ‘A’ services. The primary goal of this service is to oversee India’s corporate sector. Probationary officers are trained at the ICLS Academy, which is located on the Indian Institute of Corporate Affairs’ Manesar campus (IICA). Officers of the ICLS would get significant legal, economic, financial, and accounting training. |
| Indian Defence Accounts Service (IDAS) | The Ministry of Defense is in charge of this group. Officers in this cadre receive their first training at CENTRAD in New Delhi. Then there’s NIFM, or the National Academy Of Defence Financial Management Institute, which is based in Pune. Border Roads Organisation (BRO), Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO), and Ordnance Factories are the principal employers of IDAS cadre officers. The primary goal of this group is to audit defence accounts. The Controller General of Defence Accounts (CGDA) leads the service and also serves as Chief Accounts Officer to the heads of the DRDO, BRO, and Ordnance Factories. |
| Indian Information Service (IIS) | This is the Group ‘A’ service, which is in charge of the Indian government’s media branch. This service’s principal role is to serve as a link between the government and the general public. The Ministry of Information and Broadcasting oversees IIS. The Indian Institute of Mass Communication provides first training for this cadre’s trainees (IIMC). Officers from this cadre serve for a variety of media organisations, including DD, PIB, and AIR. |
Important Links:
New Batches
Fee structure
Scholarship Test
Best IAS Coaching in Delhi
UPSC Related Articles:
Frequently Asked Questions:
Answer. UPSC is India’s central government organisation that administers exams such as the Civil Services Exam (CSE) to recruit candidates for key government positions such as IAS, IPS, and IFS. The UPSC selects candidates for both civil and military services.
Answer. A candidate who is a citizen of India, or a subject of Nepal, Bhutan, or Tibet who settled in India before January 1, 1962; candidate who is a Graduate Degree from a recognised University; candidate who is a minimum of 21 years of age and not more than 32 years of age are eligible for UPSC Exam.
Answer. Indian Administrative Services (IAS), Indian Police Services (IPS), Indian Foreign Services (IFS), Indian Revenue Services (IRS-IT), and Indian Railway Traffic Services (IRTS) are the many job profiles under UPSC Services.
Answer. Officially known as the Civil Services Examination (CSE), the IAS exam is held every year by the Union Public Service Commission, which is the principal recruiting agency (UPSC). The Indian Administrative Service (IAS) is the country’s permanent bureaucracy and is part of the executive branch.
Answer. Yes, it is possible to pass the IAS exam without taking any classes. However, ‘everyone’ may not be the case. It is contingent on his or her ability to self-study effectively. You can pass UPSC CSE without any classroom coaching if you are proficient at self-study.
Answer. The initial base monthly compensation for an IAS official is Rs. 56,100, with the highest income now being Rs. 2,50,000 for a Cabinet Secretary.
Answer. History, Geography, Political Science / Civics, Economics, General Science – Physics, Chemistry, and Biology, Environmental Science, and Sociology are among the UPSC Prelims Subjects.
Answer. History, Geography, Politics, Economics, General Science – Physics, and Environmental Science are the basic subjects for UPSC.
Answer. The UPSC exam is one of India’s most difficult to pass, but it’s not impossible if you use the appropriate method. The UPSC exam is one of India’s most difficult to pass, but it’s not impossible if you use the appropriate method.
Answer. Yes, without couching, one year is sufficient for IAS preparation. You can pass this exam on your first attempt if you focus your studies. Preparing for UPSC is a full-time job in and of itself; you must put in at least 6-8 hours per day during your preparation.
Additional FAQs
Answer. Female applicants, Persons with Benchmark Disabilities (PwBD), and candidates belonging to the Scheduled Caste and Scheduled Tribe groups are excused from paying the Examination Fee in all of the Commission’s examinations.
Answer. The Civil Services Examination (CSE) is divided into two parts: the Civil Services (Preliminary) Examination (CSP) and the Civil Services (Main) Examination (CSE) (Written and Interview).
Answer. The exam’s question papers are of the traditional (essay) form. Each paper will take three hours to complete.
Answer. The minimal qualifying requirements for each of the two qualifying papers, English and Indian Languages, are now set at 25% in the Examination Rules.
