GS 2
A common civil code spelling equality for every Indian
Context: The 22nd Law Commission has called for responses to a proposal for a Uniform Civil Code in India.
Relevance: GS Paper – 2 Fundamental Rights Directive Principles of State Policy

The Need for a Uniform Civil Code:
- Provenance of India’s Personal Laws: The origin of India’s personal laws can be traced back to the British colonial government, which imposed them without considering the sentiments of the native population. The intention behind these laws, whether out of concern for natives’ sentiments or as a divide and rule strategy, is debatable but essential to note.
- Patriarchal Framing of Personal Laws: Personal laws in India exhibit a clear and unmistakable patriarchal framing, privileging men in various aspects. Examples include only men being allowed to be the ‘karta’ or head of a Hindu Undivided Family and Muslim women not entitled to maintenance beyond a certain period after divorce.
- Inequalities for Women: Women’s empowerment is hindered by personal laws that maintain gender-based inequalities and discrimination. In some tribes, women are denied inheritance of ancestral property, and Parsi women marrying outside the community face excommunication.
- Exclusion of LGBT Community: The LGBT community was ignored by British colonialists, and they did not even receive a personal law. Additionally, their actions were criminalized, even if consensual, reflecting the discriminatory approach.
Understanding Religious Freedom:
- Religious freedom implies the freedom to adopt the faith of one’s choice, but it does not justify extra-constitutional expressions that infringe upon democratic principles.
- The right to religion should not be used to regulate women’s autonomy or deny equal rights to different sections of the population.
Importance of Gender Equality:
- The focus should be on women’s rights within every religious group rather than seeking parity among men of different religious backgrounds.
- Equal treatment for all, irrespective of religion, is essential in a democratic society where liberty and equality should be guaranteed.
Inclusion of the LGBT Community:
- The current debate on personal law must include the LGBT community, addressing issues related to civil partnership, inheritance, and adoption for them.
- A universal civil code that encompasses all Indians, regardless of faith, gender, or sexual orientation, can empower a wide section of the population and eliminate discriminatory laws.
Conclusion:
- A Uniform Civil Code, in line with democratic principles, is crucial for ensuring justice and a fullness of life to every individual in India.
- It is time to move beyond the binary of Hindu-Muslim and recognize the need to address gender unjust laws and empower the LGBT community through a universal civil code. Such a code would align with India’s vision of creating just social, economic, and political institutions for all its citizens.
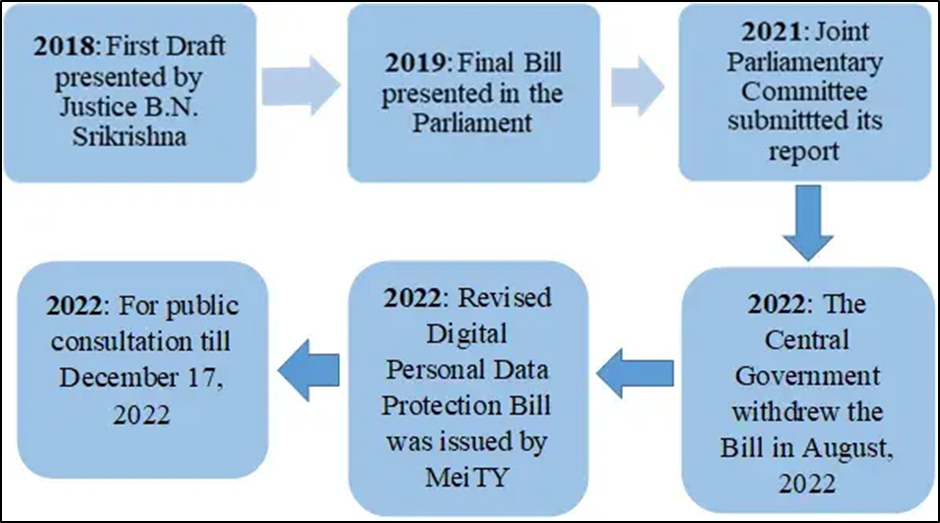
A Bill that fences in the right to information
Context: The Union Cabinet’s approval of the Digital Personal Data Protection Bill, slated for the monsoon session of Parliament, has raised concerns among citizens.
The Importance of Right to Information (RTI) Act:
- The Indian Right to Information (RTI) Act, effective since October 12, 2005, is a crucial transparency law empowering citizens and recognizing their role as owners and rulers of India.
- It resulted from people’s struggles led by the Mazdoor Kisan Shakti Sangathan, and its provisions were carefully crafted by an all-party parliamentary committee to ensure an efficient government while preserving democratic ideals.
Citizen Empowerment and Opposition from Authorities:
- Governments and those in power have been perturbed by the transfer of power to ordinary citizens through the RTI Act.
- Despite efforts to deny legitimate rights, citizens have effectively used RTI to expose wrongdoing and corruption, empowering them to hold the government accountable.
Misused Exemptions and Refusals:
- Section 8(1)(j) is the most misused exemption, allowing withholding of personal information not related to public activity or privacy invasion.
- Officials have used personal information exemptions to cover arbitrary, corrupt, or illegal acts, violating the spirit of the RTI Act.
Proposed Amendment and its Implications:
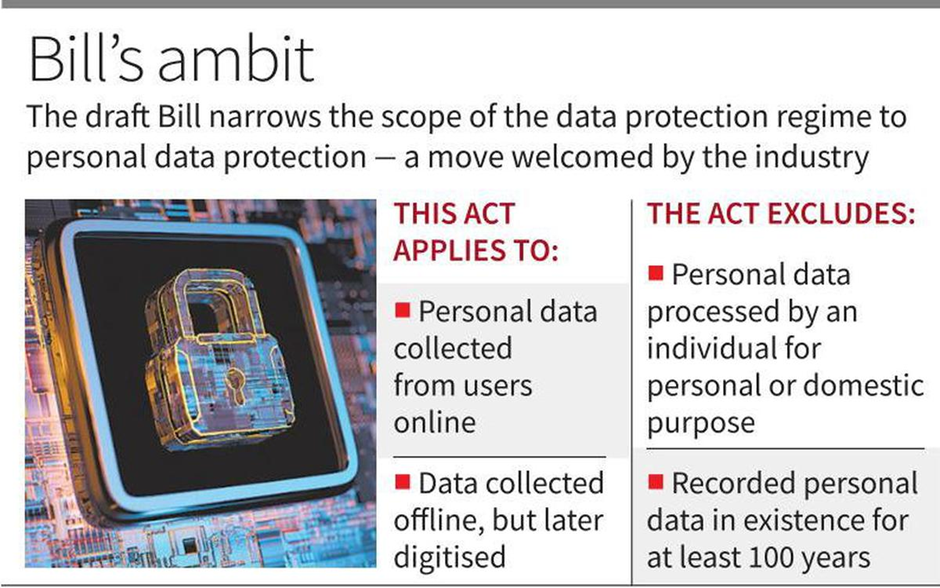
- The proposed Data Protection Bill seeks to amend RTI Act Section 8(1)(j) to exempt all information related to personal information.
- If implemented, PIOs could legally deny most information by relating it to a person, making RTI a right to deny information instead of a tool for transparency.
Threat to Democracy and Regression:
- The proposed amendment implies that current denials based solely on personal information grounds are illegal.
- The amendment could lead to a major regression for democracy, rendering RTI an ineffective tool and undermining transparency and citizen empowerment.
Conclusion:
- The proposed Digital Personal Data Protection Bill’s provisions have raised concerns about weakening citizens’ right to information.
- The RTI Act, a powerful transparency tool, has empowered citizens and exposed corruption. The proposed amendment threatens to undo the progress made in ensuring transparency and accountability in India’s democracy.
Eye on Emirati flows
Context: The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) and the Central Bank of the UAE have agreed to establish a framework for using their local currencies, the Indian rupee and the UAE dirham, for cross-border transactions.
This move aims to promote bilateral trade and reduce reliance on the US dollar as an intermediary currency for settling transactions. The agreement also includes the establishment of a Local Currency Settlement System to facilitate payments in the two currencies.
Benefits of Local Currency Settlement:
- The use of rupee and dirham for cross-border payments will reduce exchange rate risks for businesses in both countries, improving the ease of doing business and boosting trade.
- It will lead to the development of a rupee-dirham foreign exchange market, enabling independent pricing of the two currencies.
Potential for Internationalization of the Rupee:
- The India-UAE local currency settlement system could serve as a stepping stone for other bilateral currency accords and contribute to the internationalization of the Indian rupee.
- The success of this initiative will depend on its adoption by businesses in both nations.
Challenges and Opportunities:
- Emirati businesses need remunerative avenues to deploy potential rupee flows if they choose to receive payments in the Indian currency.
- UAE can potentially serve as a currency entrepôt, allowing Indian businesses to use the dirham as a gateway for transactions with other countries like Russia.
- Policymakers must be aware of the economic risks and opportunities associated with these moves, considering the rapidly evolving global environment.
Historical Ties and Pragmatic Approach:
- The UAE’s predecessor entity, the Trucial States, historically used the Indian rupee and the Gulf rupee as de facto currencies until the mid-1960s, making the reestablishment of currency ties appear natural.
- In the present global scenario, businesses will make decisions based on economic logic, and policymakers must carefully weigh the risks and opportunities while promoting currency ties.

Conclusion:
- The agreement between RBI and the Central Bank of the UAE to use local currencies for cross-border transactions is a significant step in promoting bilateral trade and reducing reliance on intermediary currencies.
- By facilitating easier cross-border payments and encouraging the use of the rupee and dirham, this move has the potential to boost trade and internationalize the Indian rupee. Policymakers must be vigilant and pragmatic in addressing challenges and seizing opportunities in this rapidly evolving global landscape.
GS 3
How are cheetahs faring in India?
Context: One of the cheetahs, nicknamed Surya, was found dead in the Kuno National Park last week.
Relevance: GS Environment

Project Cheetah:
Project Cheetah is India’s ambitious cheetah relocation program, aimed at bringing in 510 cheetahs annually over the next decade to establish a self-sustaining population of about 35 cheetahs in natural, unfenced, wild conditions.
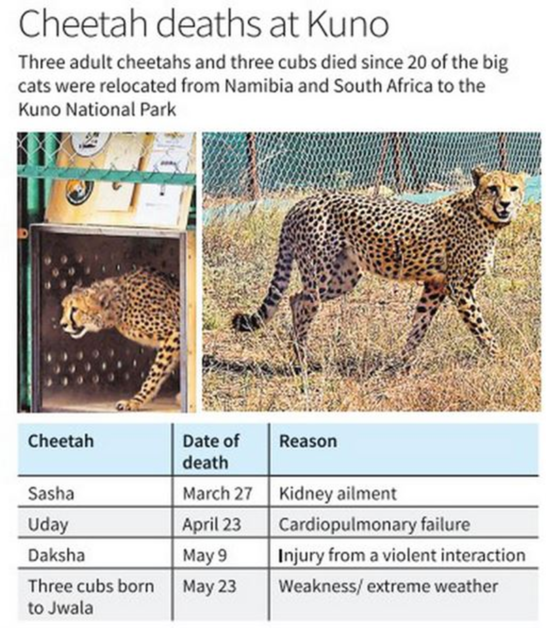
Deaths of Cheetahs in Kuno National Park:
- The recent deaths of cheetahs in Kuno National Park (KNP), Madhya Pradesh, have raised concerns about the need for a medical review.
- One cheetah, named Surya, was found dead with a wound on its neck infected with maggots, possibly caused by the radio collar fitted onto its neck.
- The Environment Ministry has dismissed suggestions of infection caused by the collar but has recommended a thorough medical examination of all surviving animals.
Cheetah Deaths and Survival Rates:
- Other cheetah deaths include Tejas attacked by another cheetah within the enclosure, cubs dying from heat and malnourishment, and an adult female dying from injuries involving a skirmish among the animals.
- Experts note that cheetah cubs in the wild have a high mortality rate, with only 10% surviving to adulthood.
- However, most deaths in Kuno occurred among the cheetahs in the “bomas,” not in the wild.
Challenges and Flaws of Project Cheetah:
- Critics point out that all 20 cheetahs in Kuno National Park is too little space and prey for the animals, considering cheetahs’ need for large distances to roam.
- Extended quarantine periods have affected the cheetahs’ adaptive capabilities and caused psychological adjustment problems, making them more vulnerable.
- Unlike tigers and leopards, cheetahs are relatively delicate animals and are more likely to be fatally injured in the wild.
- The success of Project Cheetah depends on whether the animals can successfully establish themselves in India over time, as they currently face no competition from comparable predators like lions and leopards.
Future Plans for Project Cheetah:
- There are plans to develop a second reserve in Gandhisagar, Madhya Pradesh, and establish a cheetah rehabilitation center to support the program.
Project Cheetah is a significant effort by India to reintroduce cheetahs in the wild. However, recent cheetah deaths in Kuno National Park have highlighted the need for thorough medical reviews and have raised concerns about the project’s challenges and flaws. The success of Project Cheetah will depend on addressing these issues and ensuring a conducive environment for the cheetahs to thrive in India’s natural habitats.
Prelims
U.S. hands over 105 antiquities to India following agreement
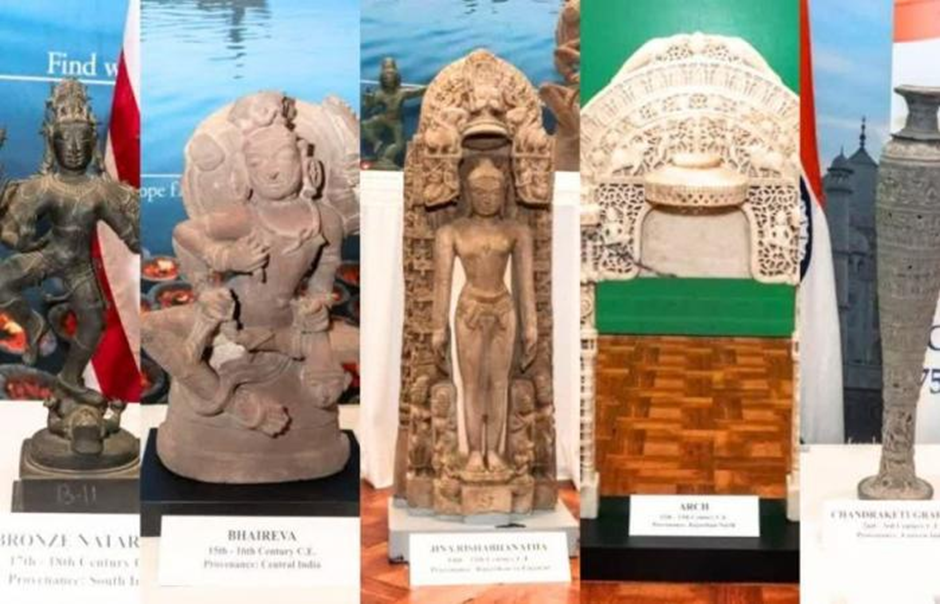

- The United States handed over 105 trafficked antiquities to India in a repatriation ceremony at the Indian Consulate in New York.
- The restitution of these artifacts follows an agreement made during Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s state visit to the U.S. last month.
- India and the U.S. have also agreed to work on a Cultural Property Agreement to prevent future illegal trafficking of cultural artifacts.
- Ambassador of India to the United States, Taranjit Singh Sandhu, highlighted the value of these artifacts to India’s living heritage and culture.
Geographical Spread and Historical Significance:
- The 105 artifacts represent a wide geographical spread, originating from different regions of India, including eastern, southern, central, northern, and western India.
- The artifacts date back to various periods, ranging from the 2nd-3rd century CE to the 18th-19th century CE, and are made of terracotta, stone, metal, and wood. Around 50 of them hold religious significance.
ISRO’s second orbit-raising manoeuvre successful
The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) successfully performed the second orbit-raising maneuver (earthbound apogee firing) of Chandrayaan-3.
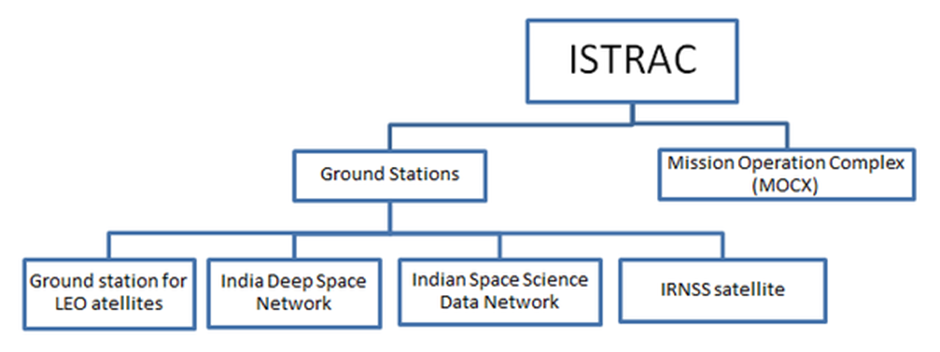
- ISRO Telemetry, Tracking and Command Network (ISTRAC), Bengaluru is entrusted with the major responsibility to provide tracking support for all the satellite and launch vehicle missions of ISRO.
- The major objectives of the centre are: carrying out mission operations of all operational remote sensing and scientific satellites, providing Telemetry, Tracking and Command (TTC) services from launch vehicle lift-off till injection of satellite into orbit and to estimate its preliminary orbit in space and hardware and software developmental activities that enhance the capabilities of ISTRAC for providing flawless TTC and Mission Operations services.
- Towards, these objectives, ISTRAC has established a network of ground stations at Bengaluru, Lucknow, Mauritius, Sriharikota, Port Blair, Thiruvananthapuram, Brunei, Biak (Indonesia) and the Deep Space Network Stations.
Webb space telescope rediscovers star-forming region
Introduction to James Webb Space Telescope (JWST)
- Launched in 2021 and operational since last year
- Marks one year since unveiling its first scientific results
- Aims to explore the universe through infrared observations
Rho Ophiuchi Cloud Complex
- Closest star-forming region to Earth
- Located in the Milky Way galaxy, approximately 390 light-years away
- Nebula serves as a nursery for new stars
- Estimated age of the nebula is around one million years
Insights into Star Formation
- JWST’s image reveals new suns and planet-forming disks
- Similarities with the early solar system over 4.5 billion years ago
- Violent outbursts during the formation of stars and planetary systems
- Dusty cocoon around young stars
JWST’s Unique Ability to Peer through Dust
- Rho Ophiuchi core hidden by large amounts of dust
- Visible light telescopes like Hubble cannot observe the core
- JWST’s infrared vision allows the detection of young stars within the cloud
Observation of Jets from Young Stars
- Material jets emanating from young stars affect surrounding gas and dust
- Molecular hydrogen lights up due to the impact of the jets
- Glowing cave created by stellar winds
JWST’s Remarkable Discoveries
- Uncovered earliest-known galaxies and black holes
- Observed mature compact galaxies with abundant stars, formed shortly after the Big Bang
Comparison with Hubble Space Telescope
- JWST is more sensitive and observes mainly in the infrared
- Hubble primarily observes at optical and ultraviolet wavelengths
- JWST’s capability to look at greater distances and further back in time
Impact on Humanity’s Understanding of the Universe
- JWST has transformed the view of the cosmos
- Observes dust clouds and captures light from distant corners of the universe

