GS 1
What does India’s first gig workers’ rights Bill stipulate?
Gig workers welfare Bill passed in Rajasthan
Source: https://www.thehindu.com/todays-paper/2023-07-25/th_chennai/articleGMLBHCFD4-3696360.ece
Context: The Rajasthan government passed the Rajasthan Platform Based Gig Workers (Registration and Welfare) Bill, 2023.
Relevance: GS 3 Economy


Purpose and Scope of the Bill:
- It is the first legislation of its kind in India outlining welfare schemes for the State’s approximately three lakh gig workers.
- The bill applies to digital aggregators and primary employers engaging platform-based gig workers in Rajasthan.
- It proposes the establishment of a Welfare Board comprising state officials, representatives from gig workers and aggregators, and others from civil society.
- The Welfare Board will set up a welfare fund, register gig workers, aggregators, and primary employers, and ensure social security for gig workers.
Funding Mechanism:
- The “Social Security and Welfare Fund” will be created, consisting of contributions from individual workers, state government aids, other sources, and a “welfare cess” deducted from each transaction by aggregators.
- The welfare cess will be between 1% to 2% of the value of each transaction, to be paid by aggregators within the first five days of each month.
- Labor unions objected to workers contributing to the fund, insisting it should come solely from aggregators and state funds due to the fluctuating and inadequate nature of gig workers’ pay.
Recognition of Workers’ Rights:
- Unlike existing labor laws, the Rajasthan Bill recognizes gig workers’ right to be registered from the moment they join an app-based platform, irrespective of the duration of work or the number of providers they work for.
- The Welfare Board will formulate schemes for social security, including accidental insurance, health insurance, and other benefits related to health, accident, and education.
Grievance Redressal:
- Gig workers have the right to be heard for any grievances related to entitlements, payments, and benefits provided under the Act.
- Workers can file petitions physically or online through the web portal, with an option for the employer to object within 90 days before an Appellate Authority.
- Challenges in current redressal mechanisms have been noted, with some gig workers protesting arbitrary account blocking and lack of support.
Accountability of Aggregators:
- Aggregators are responsible for timely depositing the welfare cess, updating the gig worker database, and documenting any changes in numbers within one month.
- Non-compliance by aggregators may result in fines ranging from ₹5 lakh to ₹50 lakh for repeated violations, with primary employers also facing penalties.
GS 2
Is there a rural bias in national surveys?
Source: https://www.thehindu.com/todays-paper/2023-07-25/th_chennai/articleGMLBHCFD8-3696359.ece
Context: The Government of India recently appointed a panel under the chairmanship of Pronab Sen, former Chief Statistician of India to review the methodology of the National Statistical Organisation (NSO).
Relevance:
Need for a review:
- Shamika Ravi and Bibek Debroy argued that outdated survey methods used in national surveys (e.g., NSS, NFHS, PLFS) have underestimated India’s development.
- P.C. Mohanan and Amitabh Kundu, however, disagreed and stated that there is no systematic underestimation of development, but they acknowledge the presence of errors that should be minimized.
- National-level data is crucial for research, policymaking, and development planning, making it essential to analyze these claims in light of existing evidence.
Importance of National Family Health Survey (NFHS) Data:
- NFHS data, conducted by the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare with IIPS, is a valuable resource for understanding India’s development over 30 years.
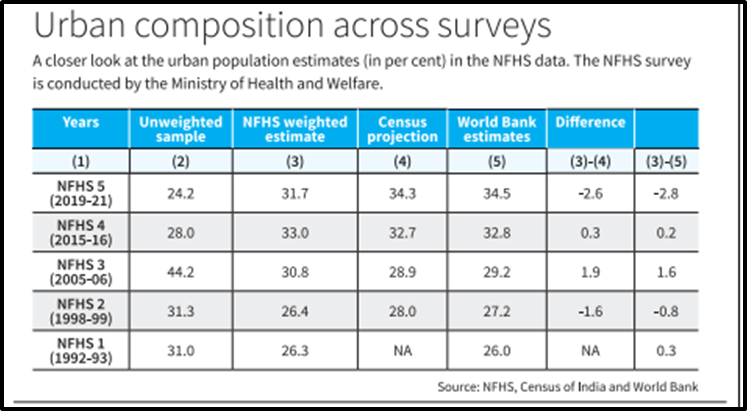
Debunking the Rural Bias Claim:
- Ms. Ravi and Mr. Debroy argued that NFHS exhibits a rural bias, overestimating the rural population due to heavy reliance on last Census data.
- Examination of five rounds of NFHS data did not support this claim; there was no systematic rural bias in representation.
- Instead, errors in rural and urban population estimation seem random rather than systematic.
Minimizing Errors in NFHS Data:
- Urban areas tend to have higher percentages of no-response compared to rural areas, but this doesn’t show a clear relation to rural or urban bias in estimation.
- Improvements can be made in minimizing errors and assigning appropriate sample weights to correct underrepresentation of rural or urban populations.
Recommendations for the Pronab Sen Committee:
- The committee should address concerns to make the sample adequately representative without completely overhauling the survey methodology.
- Avoid importing systematic urban bias into national level surveys in the name of removing non-existent systematic rural bias.
ASEAN, a persistence with dialogue, on a trodden path
Source: https://www.thehindu.com/todays-paper/2023-07-25/th_chennai/articleG9KBHCMHF-3696271.ece
Context: The 56th Foreign Ministers Meeting (FMM) of ASEAN held in Jakarta in July 2023 provided insights into the region’s dynamics.
Relevance: GS 2 International Organisations
Challenges to ASEAN’s Vision
- Challenges arise due to internal differences on issues like Myanmar and strained relations between the US and China.
- China’s close relations with certain ASEAN states influence the group’s stance on the South China Sea issue.
- ASEAN’s diplomatic dilemma arises from the acrimonious US-China debate, impacting its leadership and agenda-setting ability.
ASEAN Outlook on the Indo-Pacific (AOIP)
- ASEAN supports the AOIP, focusing on maritime cooperation, connectivity, UN Sustainable Development Goals, and economic collaboration.
- However, concerns persist about the implementation of the AOIP.
Unity and Centrality
- ASEAN’s credibility and centrality depend on adhering to the ASEAN Charter and steering regional dynamics.
- Internal disunity, especially regarding Myanmar, challenges ASEAN’s ability to maintain centrality.
India’s Role in the Indo-Pacific
- India recognizes the significance of a “strong and unified” ASEAN in the emerging Indo-Pacific dynamics.
- India emphasizes convergence between the AOIP and its Indo-Pacific Oceans Initiative.
- External Affairs Minister S. Jaishankar highlights the importance of newer areas of collaboration, such as cyber, financial, and maritime security domains.
Prospects for the Future
The next ASEAN summit in Jakarta in September 2023 is expected to address challenges and offer greater clarity on regional cooperation.
India’s ties with Sri Lanka are bound by the Tamil question
Source: https://www.thehindu.com/todays-paper/2023-07-25/th_chennai/articleG9KBHCMHJ-3696269.ece
Context: Prime Minister Narendra Modi and Sri Lankan President Ranil Wickremesinghe met in Delhi last week.
Relevance: GS 2 International Relations

Joint Statement on Economic Cooperation
- India and Sri Lanka outlined a forward-looking vision for their relations through a joint statement titled “Promoting Connectivity, Catalyzing Prosperity: India-Sri Lanka Economic Partnership Vision.”
- The statement covers five areas of cooperation: maritime, air, energy, trade, and people-to-people initiatives.
- Key initiatives include investments in maritime and air connectivity, development of renewable energy projects, increased trade, and Indian support for Sri Lanka’s economy.
Omissions in the Vision Statement
- Notably, the statement does not acknowledge previous commitments by Sri Lanka regarding the 13A constitutional amendment for devolution of powers to the North and Eastern provinces.
- The issue of resolving long-pending matters related to the arrest of Indian fishermen was also left unaddressed in the statement.
Prime Minister Modi’s Appeal
- In his speech, Prime Minister Narendra Modi made a sharp appeal for devolution and the conduct of Provincial Council elections, emphasizing the need for a “life of respect and dignity” for the Sri Lankan Tamil community.
Sri Lanka’s Response
- The ruling SLPP in Colombo indicated that the government lacks the electoral mandate to discuss the devolution and Tamil issue with India.
- This suggests that Sri Lanka is not willing to bring historical concerns over the Tamil issue into bilateral negotiations with India.
Implications and Concerns
- The joint statement’s omissions regarding the devolution and Tamil issue raise concerns about the completeness of the vision for the future relationship between India and Sri Lanka.
- The historical ties between the two countries have faced challenges in the past, and an amicable resolution of these issues is crucial for a comprehensive vision moving forward.
GS 3
Semiconductors: what exactly is India going to manufacture?
Source: https://www.thehindu.com/todays-paper/2023-07-25/th_chennai/articleGMLBHCF47-3696353.ece
Context: India aims to gain access to semiconductor technologies to create highly skilled jobs and become part of an elite group of nations.
Relevance: GS -3 Science and Technology – developments and their applications and effects in everyday life
Understanding Semiconductors and Transistors
- A semiconductor chip consists of transistors crafted from materials like silicon.
- Transistors encode and manipulate data in the form of 0s and 1s through the source, gate, and drain.
- Semiconductor chips store information in bits represented by voltage levels.
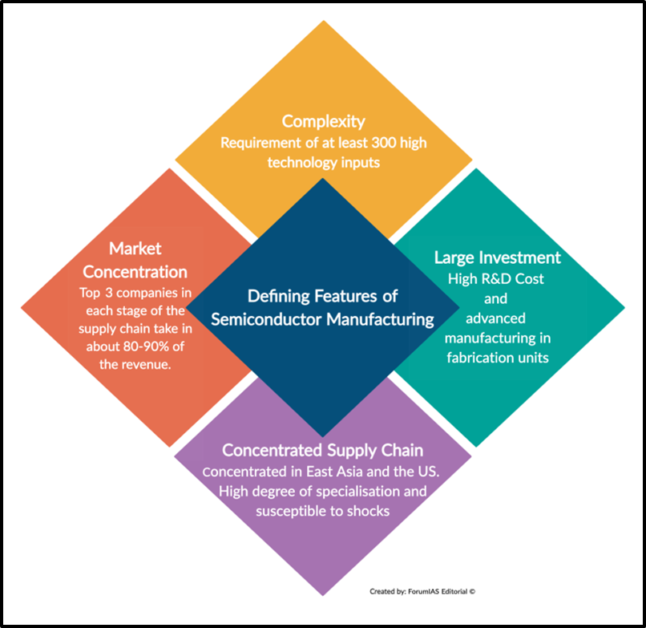
Node Number Explanation
- The names of semiconductor nodes are based on the length of the gate and the distance between adjacent metal strips (pitch).
- Shrinking transistors led to faster operation but caused challenges in reducing the size of metal wires.
- The naming convention for nodes changed over time due to advancements in miniaturization.
Significance of Node Numbers
- Node names do not directly represent physical dimensions but are used by marketers to indicate progress and improvements.
- Different companies may use the “nm” unit in node names to mean different things.
Importance of Legacy Nodes for India
- India’s focus is on nodes of 28 nm or higher, not outdated chips.
- Legacy nodes (28 nm and higher) offer advantages for applications like robotics, defense, IoT, and automotive sectors due to cost-effectiveness.
- Even advanced fabrication facilities maintain production of legacy nodes to meet demand in various industries.
Long-term Success and Electric Cars
- Starting with legacy nodes can help India prepare for long-term success in the semiconductor industry.
- The demand for legacy nodes will increase with the rise of electric cars and complementary electronics.
India’s Semiconductor Journey
- The Indian government and private players are wise to begin their semiconductor journey with legacy nodes and improve over time.
- India has the potential to become a significant hub for semiconductors in the future.
A big step in reducing the risk of disasters
Source: https://www.thehindu.com/todays-paper/2023-07-25/th_chennai/articleGMLBHCEQM-3696276.ece
Context: Disasters around the world are claiming more and more lives.
Relevance: GS 3 Disaster Management
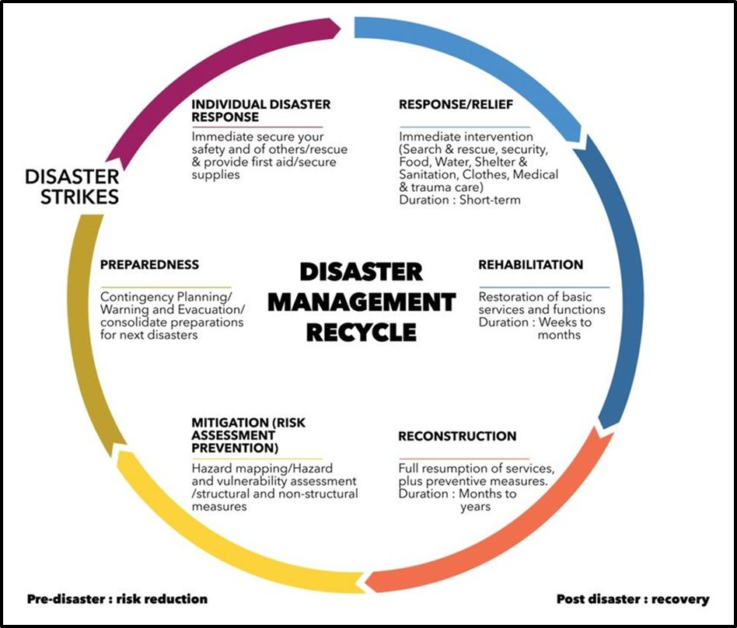
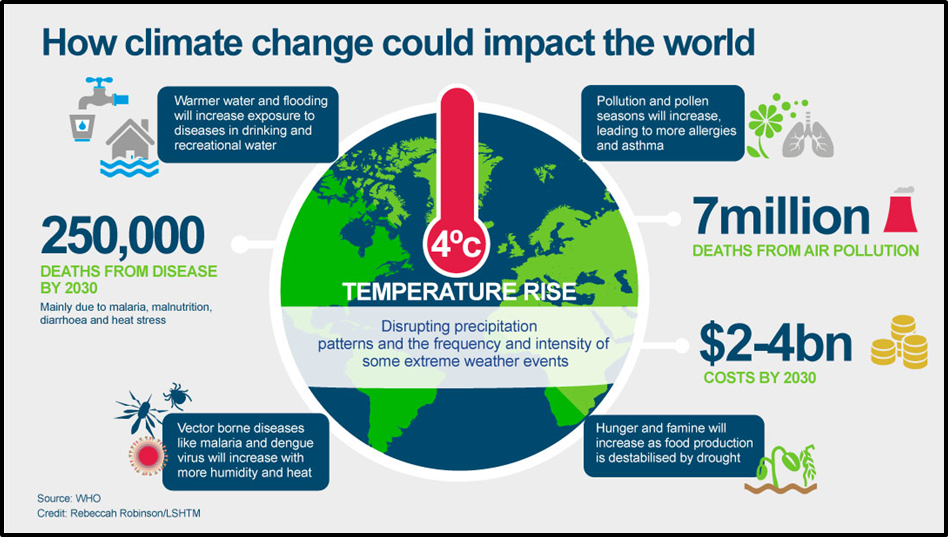
Increasing Disasters and Climate Change Consequences
- Disasters worldwide, such as heatwaves, wildfires, and floods, are claiming more lives due to climate change.
- The world needs to focus on disaster prevention rather than just response to reduce losses.
India’s Initiative for Disaster Risk Reduction
- India has elevated disaster risk reduction as a priority for the G20 during its presidency.
- The G20, representing a significant portion of global GDP and population, can lead in disaster risk-informed decision-making.
Priorities Identified by the G20 Disaster Risk Reduction Working Group
- The G20 aims to enhance early warning systems, resilient infrastructure, and financing for disaster risk reduction.
- Inclusive and multi-hazard early warning systems are effective in reducing disaster deaths and economic losses.
Expanding Early Warning Systems
- The UN Secretary General’s Early Warnings for All Initiative aims for universal coverage by 2027.
- Disruptive technologies can help countries leapfrog into global forecasting capacity.
Enhancing Infrastructure Resilience
- Countries need to assess and enhance the resilience of critical infrastructure to withstand climate and disaster risks.
- Infrastructure, if built well, can contribute to sustainable development outcomes.
Coalition for Disaster Resilient Infrastructure
- India launched the Coalition for Disaster Resilient Infrastructure in collaboration with the UN to support disaster-resilient infrastructure in developing countries.
- A global methodology for infrastructure resilience reviews and stress testing is being developed based on the Principles for Resilient Infrastructure.
Transforming Risk Reduction Plans into Actions
- A new approach to financing disaster risk reduction is needed, involving finance and economy ministries along with the private sector.
- G20 nations like Indonesia and India have used risk metrics to allocate resources for disaster risk reduction at sub-national and local levels
Scaling Up Ecosystem-Based Approaches and Response Capacities
- The responsibility of scaling up ecosystem-based approaches and enhancing response capacities will be taken up by future G20 presidents.
- Brazil, the next G20 president, has committed to continuing the working group and building on India’s efforts.
Prelims
ISRO to launch PSLV-C56 carrying Singapore’s new imaging satellite
Source: https://www.thehindu.com/todays-paper/2023-07-25/th_chennai/articleG9KBHD80F-3696263.ece
Context: The Indian Space Research Organisation announced that the PSLV-C56 carrying Singapore’s DS-SAR satellite will be launched on July 30 from Sriharikota.
Relevance: GS -3 Space
Payloads and Configuration
- PSLV-C56 will carry a total of seven satellites, including the DS-SAR satellite.
- The PSLV-C56 is configured in its core-alone mode, similar to the C55 mission.
DS-SAR Satellite
- The DS-SAR satellite weighs 360 kg and will be placed in a near-equatorial orbit at 5 degrees inclination and 535 km altitude.
- It is developed under a partnership between DSTA (representing the Government of Singapore) and ST Engineering.
- DS-SAR will support satellite imagery requirements for various agencies within the Government of Singapore.
- It carries a Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) payload developed by Israel Aerospace Industries, enabling all-weather day and night imaging at 1m resolution with full polarimetry.
Other Satellites
The six other satellites include:
- VELOX-AM: A 23 kg technology demonstration microsatellite.
- Atmospheric Coupling and Dynamics Explorer (ARCADE): An experimental satellite.
- SCOOB-II: A 3U nanosatellite with a technology demonstrator payload.
- NuLIoN by NuSpace: An advanced 3U nanosatellite for seamless IoT connectivity in urban and remote locations.
- Galassia-2: A 3U nanosatellite orbiting at low earth orbit.
- ORB-12 STRIDER: A satellite developed under international collaboration.
Govt launches meri maati, mera desh campaign
Source:
Context: The Union government has launched the ‘Meri Maati Mera Desh’ campaign, envisaged as a culminating event of the ‘Azadi Ka Amrit Mahotsav’ celebration of 75 years of Indian Independence, in which soil collected from different parts of the country in August will be used to develop a garden along the Kartavya Path in Delhi.
Planned Events
- The campaign events will be organized at different levels, including panchayat, village, block, urban local body, and state and national levels.
- Panchayat-level programs will be held between August 9 and 15.
Five-Point Agenda
- The campaign’s five-point agenda includes the installation of a shilaphalakam (memorial plaque) bearing the names of those who have made the supreme sacrifice.
- Veers (bravehearts) to be honored include freedom fighters, defense personnel, Central Armed Police Forces (CAPF) personnel, and State Police who have contributed to the nation.
